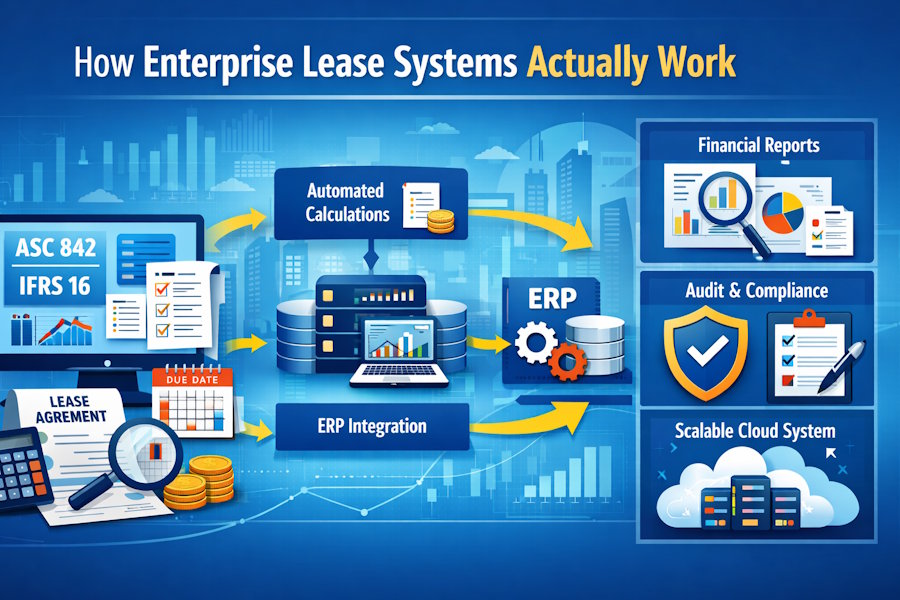
Enterprise lease management systems might sound dry, but behind the scenes they’re powerful financial engines. These platforms handle the heavy math and compliance rules that keep companies aligned with accounting standards like ASC 842 and IFRS 16. Once those standards required leases to appear on balance sheets, spreadsheets simply couldn’t keep up.
Today’s systems centralize lease data, automate complex calculations, and integrate directly with enterprise accounting software. Instead of manually tracking payments and recalculating liabilities every time a contract changes, organizations rely on structured, rule-driven technology designed for precision and scale.
Why Lease Accounting Became Technical
Lease accounting used to be relatively straightforward. Now, companies must calculate the present value of future lease payments and record both a right-of-use (ROU) asset and a lease liability. That requires discount rates, amortization schedules, and consistent remeasurement when terms change.
Enterprise lease systems automate these calculations using financial modeling engines. When a lease is modified—say the term is extended or payments are adjusted—the system recalculates liability balances instantly. This eliminates the risk of inconsistent formulas or broken spreadsheet links.
Platforms such as LeaseQuery are built around configurable accounting logic. They adapt to both U.S. GAAP and IFRS requirements and maintain audit trails for every change. The goal isn’t just automation—it’s defensible accuracy.
What’s Under the Hood
At the core of every enterprise lease system is a structured database. This database stores contract details such as payment schedules, escalation clauses, renewal options, asset classifications, and vendor information. Data normalization prevents duplication and ensures that every record ties back correctly to related entries.
Above the database sits the calculation engine. This is where discounted cash flow modeling happens. The engine processes fixed payments, variable rent components, residual value guarantees, and discount rates using high-precision decimal handling. Even small rounding errors can affect financial statements, so these systems are engineered for exactness.
The application layer manages workflows. It guides users through lease setup, enforces validation rules, and applies classification logic automatically. If a lease meets finance lease criteria under accounting standards, the system flags and treats it accordingly.
In short, it’s less like a spreadsheet and more like a purpose-built financial calculator with governance controls built in.
Integration With the Rest of Finance
Enterprise lease management doesn’t operate in isolation. It connects directly to broader financial systems.
Modern platforms typically synchronize:
- Monthly journal entries for interest and amortization
- Accounts payable schedules for recurring payments
- Fixed asset registers for ROU asset tracking
- General ledger balances for financial reporting
This integration reduces manual reconciliation. Journal entries are generated automatically and exported to ERP systems, ensuring consistency across financial statements.
APIs and middleware connectors handle secure data exchange. Whether synchronization occurs in scheduled batches or near real time, the objective is the same—maintain alignment between lease data and corporate accounting records.
Automation That Reduces Risk
One of the biggest advantages of enterprise lease systems is workflow automation. Instead of relying on calendar reminders and manual review, the system actively manages lease lifecycles.
Core automation features often include:
- Automatic recalculation when discount rates or lease terms change
- Built-in alerts for upcoming expirations and renewal deadlines
- Structured audit logs that record every modification
- Auto-generated disclosure reports for compliance filings
These controls strengthen governance. Every data change is time-stamped and traceable, which simplifies internal audits and external reviews.
Automation doesn’t just save time—it reduces the likelihood of material misstatements.
Reporting That Makes Sense
Lease standards require detailed disclosures. Organizations must present maturity analyses, weighted-average discount rates, roll-forwards of liabilities, and more.
Enterprise lease systems generate these reports directly from validated data. Instead of assembling disclosure tables manually, finance teams can produce standardized outputs with a few clicks.
Dashboards provide high-level summaries of total lease exposure across regions, asset classes, or subsidiaries. Executives gain visibility into long-term obligations without digging through raw spreadsheets.
Because calculations originate from a controlled system, reporting remains consistent and audit-ready.
Security and Governance Built In
Lease portfolios represent significant financial commitments. Strong security controls are non-negotiable.
Enterprise systems incorporate role-based permissions so users only access relevant data. Segregation-of-duties frameworks prevent unauthorized approval of lease changes. Encryption protects sensitive financial information both in storage and during transmission.
Cloud-based infrastructure adds scalability and resilience. Distributed hosting environments provide uptime reliability while allowing automatic updates when regulatory rules evolve.
Security isn’t an add-on—it’s part of the core architecture.
AI and Smarter Contract Processing
Newer systems are becoming even more intelligent. Optical character recognition (OCR) and natural language processing (NLP) tools can extract lease terms directly from uploaded contracts. Instead of manually entering payment schedules, users review and validate data that the system has already identified.
Machine learning improves extraction accuracy over time. As finance teams correct inputs, the system refines its recognition patterns.
Some platforms also offer scenario modeling tools. Finance leaders can simulate interest rate changes or portfolio expansions to see how lease liabilities shift. This turns lease data into a strategic planning resource rather than just a compliance obligation.
Built for Scale
Large enterprises often manage leases across multiple countries and currencies. Enterprise systems support multi-currency conversions, consolidated reporting, and jurisdiction-specific accounting treatments.
Cloud-native architecture allows elastic storage and processing capacity. As portfolios grow, performance remains stable. Calculation speed, data integrity, and reporting accuracy are preserved even as transaction volumes increase.
Scalability ensures the system continues functioning efficiently whether an organization manages 50 leases or 5,000.
Final Takeaway
Enterprise lease management systems are sophisticated financial platforms designed to handle regulatory complexity with precision. They combine structured databases, advanced calculation engines, workflow automation, ERP integration, and emerging AI capabilities to manage lease portfolios accurately and transparently.
What might appear to be simple rent tracking is actually a highly engineered process. Behind every balance sheet line item is a system built to calculate, validate, and report lease obligations at enterprise scale—with speed, security, and reliability.