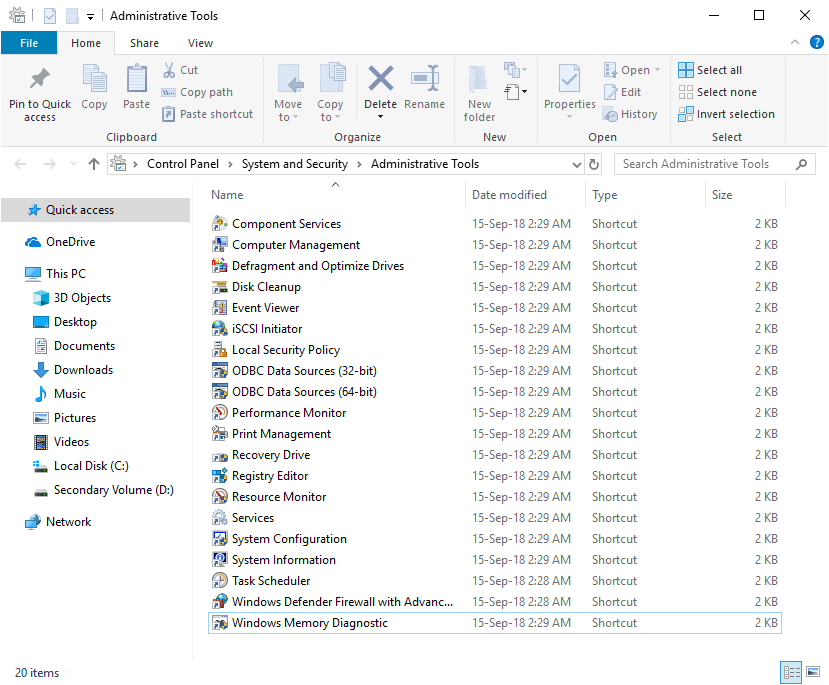
Administrative Tools is the collective name for several advanced tools in Windows that are used mainly by system administrators. This collection can be found in Windows 10, Windows 8, Windows 7, Windows Vista, Windows XP, and Windows Server operating system. In case that you are working on some optimization tool for windows or you are just creating shortcuts for tools you need in some app, this trick to open the mentioned directory may be useful for your collection. The tools were included in versions of Windows and the associated documentation for each tool should help you use these tools in Windows. The following list links to the official documentation of every tool:
- Component Services
- Computer Management
- Defragment and Optimize Drives
- Disk Cleanup
- Event Viewer
- iSCSI Initiator
- Local Security Policy
- ODBC Data Sources
- Performance Monitor
- Print Management
- Resource Monitor
- Services
- System Configuration
- System Information
- Task Scheduler
- Windows Firewall with Advanced Security
- Windows Memory Diagnostic
The following short snippet should to the trick to open the administrative tools directory in any version of Windows (where the collection is available):
// Include diagnostics namespace at the beginning of your class
using System.Diagnostics;
// Create a new process that
Process pProcess = new Process();
// e.g C:\WINNT\System32 or C:\Windows\System32
// run namely the C:\Windows\System32\control.exe file with the admintools argument
pProcess.StartInfo.FileName = Environment.SystemDirectory + "\\control.exe";
pProcess.StartInfo.Arguments = "admintools";
pProcess.StartInfo.UseShellExecute = true;
// Start process
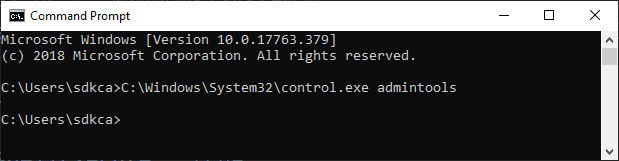
pProcess.Start();What we are doing under the hood is basically to run the control.exe executable located in the system directory with the admintools argument, which is basically the same as running the following command in the command line:
Happy coding !